# LoRa gateway
# What is a LoRa gateway
A LoRa (Long Range) gateway is a device that facilitates communication between LoRa nodes and networks, enabling the transmission and reception of data over long distances using the LoRa modulation technique. It's designed to work with devices that utilize LoRa technology, such as the MakerFab soil and moisture sensor, devices from PricelessTookit and DIY sensors.
The primary distinction between a LoRa gateway and a LoRaWAN gateway lies in the protocol and network architecture:
LoRa gateway: Focuses solely on the physical layer, utilizing the LoRa modulation for communication. It's responsible for receiving and transmitting raw LoRa signals without concerning itself with network protocols or data handling at higher layers. Being focused solely on the physical layer, a LoRa gateway offers greater flexibility for customization and experimentation. The OpenMQTTGateway LoRa gateway receives raw LoRa signals, processes them, and publishes the data to an MQTT topic. Conversely, it can subscribe to MQTT topics and send commands to LoRa devices. This gateway is particularly useful for DIY projects, home automation enthusiasts, and scenarios where direct integration of LoRa devices with MQTT is desired.
LoRaWAN gateway: Operates at a higher layer and is part of the LoRaWAN network architecture. LoRaWAN is a protocol specification built on top of the LoRa technology, providing features like adaptive data rate, encryption, and multi-channel/multi-modulation. A LoRaWAN gateway handles the data from multiple LoRa nodes, forwards it to a centralized network server, which then manages the data and communicates back to the nodes.
In essence, while both gateways utilize LoRa technology for communication, a LoRaWAN gateway is more sophisticated, offering advanced features and integration with the LoRaWAN network infrastructure. The LoRa gateway, with its simpler architecture, is ideal for small networks of nodes, offering easier setup and configuration, making it an interesting choice for users keen on experimenting with LoRa technology.
# Configuring the LoRa gateway
The LoRa gateway can be configured by MQTT commands or by using the WebUI, here are the parameters available, they can be combined with the key "save" or "erase":
- txpower: 0 to 14
- spreadingfactor: 7 to 12
- frequency: 433000000, 868000000, 915000000
- signalbandwidth: 7800, 10400, 15500, 20800, 31250, 41700, 62500, 125000, and 250000
- codingrate: 5 to 8
- preamblelength: 6 to 65535
- syncword: byte
- enablecrc: boolean
- invertiq: boolean
- onlyknown: boolean
With the WebUI:
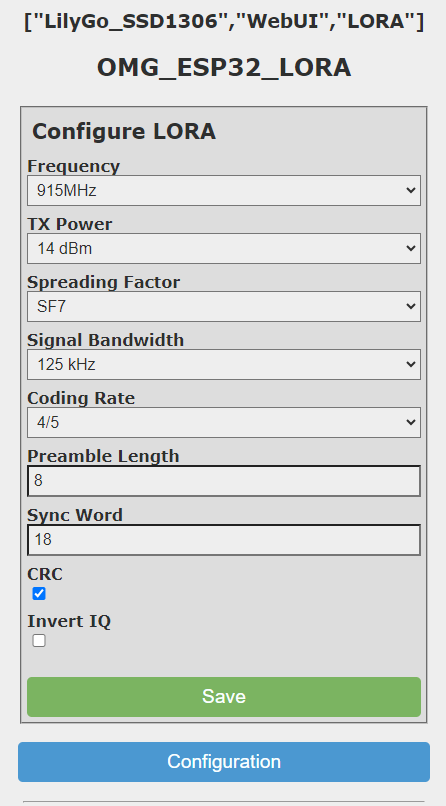
With MQTT commands:
mosquitto_pub -t home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoLORA/config -m '{"frequency":"433000000","save":true}'
# Receiving data from LoRa signal
Subscribe to all the messages with mosquitto or open your MQTT client software:
sudo mosquitto_sub -t +/# -v
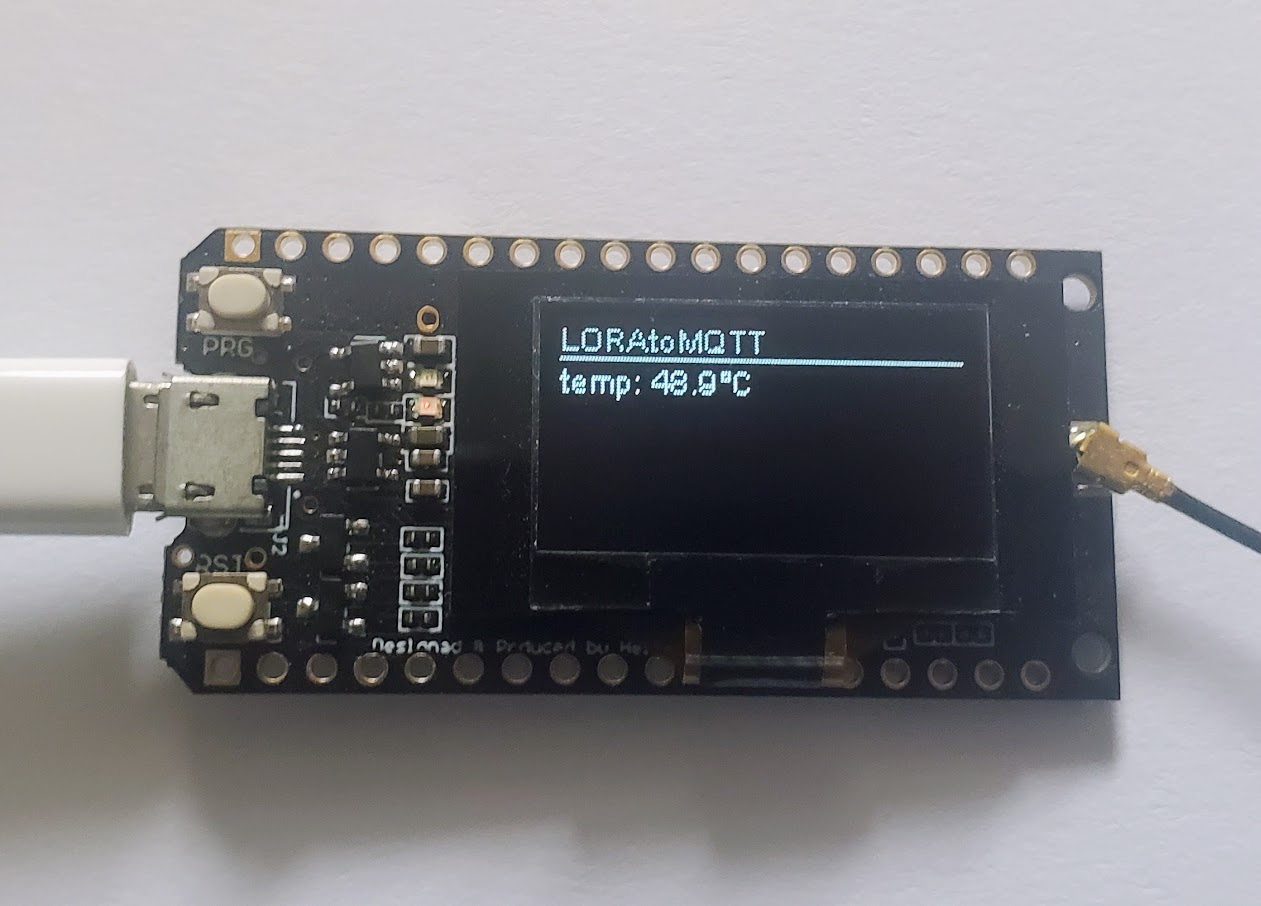
Generate your LoRa signals by using another LoRa module, you can flash the sender program from this example to an ESP32 LoRa board, this sample node will generate a LoRa signal containing the ESP32 internal temperature.
Once one board flashed with OMG and the other with the sender program you should receive regular packets into home/OpenMQTTGateway_ESP32_LORA_TEST/LORAtoMQTT/AABBCCDDEEFF like below:
{"id":"AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF","rssi":-16,"snr":9.25,"pferror":-3598,"packetSize":9,"tempc":"55.3"}
{"id":"AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF","rssi":-26,"snr":9,"pferror":-3598,"packetSize":9,"tempc":"55.4"}
{"id":"AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF","rssi":-16,"snr":9.5,"pferror":-3581,"packetSize":9,"tempc":"57"}
2
3

Messages that contain non-printable characters will be converted to hexadecimal and look like this:
{"rssi":-121,"snr":-11.75,"pferror":-29116,"packetSize":3,"hex":"C0FFEE"}
They can be filtered by setting the "onlyknown" command to true or by an activation into the WebUI or Home Assistant.
And from a supported device (in this case, a WiPhone), looks like this:
{"rssi":-50,"snr":9.25,"pferror":20728,"packetSize":30,"from":"123ABC","to":"000000","message":"Hi from WiPhone","type":"WiPhone"}
# Send data by MQTT to convert it on LoRa signal
mosquitto_pub -t home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoLORA -m '{"message":"hello OMG1"}'
This command will send by LoRa the message "hello OMG1" and use the default parameters defined in config_LORA.h (opens new window)

If you want to test that your sending works you can use another TTGO LoRa module, you can flash the receiver program from this repository (opens new window) and the SSD1306 library there (opens new window)
# Send data by MQTT with advanced LoRa parameters
- Plain text message:
mosquitto_pub -t home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoLORA -m '{"message":"test8","txpower":17}'
will make LoRa use the a txpower of 17 when sending the message "test8" - Binary message:
mosquitto_pub -t "home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoLORA" -m '{"hex":"01C0FFEE"}'
will send binary 0x01C0FFEE - WiPhone message:
mosquitto_pub -t "home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoLORA" -m '{"message":"test","type":"WiPhone","to":"123ABC","from":"FFFFFF"}'
will send "test" to a WiPhone with chip ID 123ABC
More info on where the LoRa library is born @sandeepmistry (opens new window)
Tutorial on how to leverage LoRa for a mailbox sensor from PricelessToolkit (opens new window):