# RF gateways (433mhz/315mhz/868mhz/915mhz)
# What is an RF gateway
An RF (Radio Frequency) gateway is a device that facilitates communication between RF devices and other communication protocols, such as MQTT in this context. Operating at specific frequencies like 433MHz, 315MHz, 868MHz, and 915MHz, these gateways can receive signals from various RF devices, decode them, and then forward the decoded data to systems like Home Assistant, OpenHAB, or any other MQTT-based system.
The primary advantage of using an RF gateway is its ability to bridge the gap between the world of RF devices, which might include sensors, remote controls, and other RF-based gadgets, and modern smart home systems or applications. This enables users to integrate a wide range of devices into their smart home setup, even if those devices were not originally designed for such integration.
In the context of the 433MHz MQTT gateway, the device not only decodes RF signals but also allows for seamless integration with MQTT systems. This means that signals from RF devices can be easily published to MQTT topics, and likewise, MQTT messages can be translated into RF signals for transmission. This two-way communication capability makes the gateway a powerful tool for expanding the capabilities of both RF devices and MQTT systems.
OpenMQTTGateway leverages several libraries for RF communication:
| Library | Description | Device Support | Resource Requirements | Flexibility | Integration Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RTL_433 | Maintained and performant library supporting receiving 433Mhz but also other frequencies (does not support sending) | Wide range of devices | Moderate | Decodes various protocols | Can be integrated with systems supporting Home Assistant Auto Discovery |
| RCSwitch | Arduino library for 433MHz module communication. | Basic devices | Lightweight | Basic encoding and decoding | Basic integration |
| Pilight | Open-source solution for device control and data retrieval. | Broad range of devices and protocols | Moderate | Offers raw and protocol-specific data handling | Structured data |
| RF2 | Library focused on KaKu devices and protocol. | Specific devices and protocols | Lightweight | Decoding and encoding capabilities | Basic integration |
INFO
RTL_433 library can only receive data, RCSwitch, PiLight, RF2 can receive and transmit.
# Common parameters accross modules
# Change default frequency (SX127X and CC1101)
The frequency can be can changed by sending an MQTT message or through the WebUI. Parameter is frequency and valid values are 300-348 Mhz, 387-464Mhz and 779-928Mhz. Actual frequency support will depend on your board
home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoRF/config {"frequency":315.026}
Note that with CC1101 this frequency will be used as the default sending frequency.
# Changing Active Receiver Modules
Switching of the active transceiver (RTL_433 receiver only) module is available between the RF, RF2, and (RTL_433 or Pilight) gateway modules, allowing for changing of signal decoders without redeploying the OpenMQTTGateway package. Sending a JSON message to the command topic will change the active transceiver module.
To change the RF gateway module, which will receive, send a json message to the RF gateway module command subject (home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoRF/config) with the corresponding value of the key "active"
1 - PiLight
2 - RF
3 - RTL_433
4 - RF2
Example to receive from the RF gateway:
mosquitto_pub -t "home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoRF/config" -m '{"active":2}'
Example to receive from the Pilight gateway:
mosquitto_pub -t "home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoRF/config" -m '{"active":1}'
The active receiver can also be changed with the WebUI.
The OpenMQTTGateway RFtoMQTT status message contains a key active which is the current active receiver module.
There is example configuration entry for Homea Assistant in the intergrations doc.
# RTL_433 device decoders
This feature is only available on a ESP32 based device with a supported transceiver connected due to the resource requirements of the rtl_433 device decoders. At the present time only Pulse Position Modulation (OOK_PPM), Pulse Width Modulation (OOK_PWM) and Pulse Manchester Zero Bit (OOK_PULSE_MANCHESTER_ZEROBIT) based decoders are available.
# Supported hardware combinations
- ESP32 based device with a CC1101 transceiver
- Heltec WiFi LoRa 32 (V2.1) and LilyGo LoRa 32 V2.1
- ESP32 DOIT DevKit V1 and Ai-Thinker R01 (SX1278)
- ESP32 + SX1278/SX1276
# Supported Decoders
For the most recent support decoder list please check the rtl_433_esp (opens new window) repository.
# Change Signal RSSI Threshold Delta
Delta applied to RSSI floor noise level to determine start and end of signal, defaults to 9db.
home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoRF/config {"rssithreshold": 9}
# Retrieve current status of receiver
home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoRF/config {"status":1}
{"model":"status",
"protocol":"debug",
"debug":0, - rtl_433 verbose setting
"duration":11799327, - duration of current signal
"Gap length":-943575, - duration of gap between current signal
"rssi":-38, - most recent received signal strength
"train":1, - signal processing train #
"messageCount":3, - total number of signals received
"totalSignals":9, - RegOokFix signal quality count ( of 10 )
"ignoredSignals":0, - RegOokFix signal quality ignored signals
"unparsedSignals":3, - RegOokFix signal quality unparseable signals
"_enabledReceiver":1, - which receiver is enabled
"receiveMode":0, - is the receiver currently receiving a signal
"currentRssi":-89, - current rssi level
"rssiThreshold":-82, - minimum rssi level to start signal processing
"pulses":0, - how many pulses have been received in the current signal
"StackHighWaterMark":5528, - ESP32 Stack
"freeMem":112880} - ESP32 memory available
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# RCSwitch based gateway
The RCSwitch (opens new window) library is an Arduino library that facilitates communication with 433MHz RF modules. It is designed to be lightweight and easy to use, making it suitable for basic RF communication tasks. The library supports both sending and receiving of RF signals, allowing for integration with various RF devices such as remote controls, sensors, and switches.
To enable this module during compilation, add the flag '-DZgatewayRF="RF"' or uncomment the line #define ZgatewayRF "RF" in the User_config.h file.
Other useful definitions can be:
#define RF_DISABLE_TRANSMITTo disable the transmit functions and free up the pin for other uses, add (or uncomment) this line to theconfig_rf.hfile.#define repeatRFwMQTT trueTo enable repeating the RF signal received by the gateway, set this parameter to true in theconfig_rf.hfile.#define RF_on_HAS_as_DeviceTriggerTo send a Home Assistant Device Trigger Message for each RF signal received, add (or uncomment) this line in theconfig_rf.hfile. Note that this action also depends on theZmqttDiscoverysettings.#define RF_on_HAS_as_MQTTSensorTo send a Home Assistant MQTT sensor message for each RF signal received, add (or uncomment) this line in theconfig_rf.hfile. Note that this action also depends on theZmqttDiscoverysettings.
# Handling RF signal over MQTT
In this chapter, the process of receiving and sending RF signals using MQTT will be explored. By subscribing to MQTT topics and publishing messages, RF devices can be seamlessly integrated with an MQTT broker.
# Receiving Data from RF Signal
To receive data from an RF signal, follow these steps:
Subscribe to all messages using mosquitto or open your MQTT client software:
sudo mosquitto_sub -t +/# -v1Generate your RF signals by pressing a remote button or other RF device. You should see output similar to:
home/OpenMQTTGateway/433toMQTT {"value":1315156,"protocol":1,"length":24,"delay":317}1
# Send data by MQTT to convert it to an RF signal
To send an RF signal using MQTT, you can publish a message to the topic home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTto433 with the desired value. For example:
mosquitto_pub -t "home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTto433" -m '{"value":1315156}'
This command will send the RF code 1315156 using the default parameters (protocol 1, delay 350).
When publishing data via MQTT, the Arduino IDE serial monitor will display the received value and the corresponding MQTT topic:
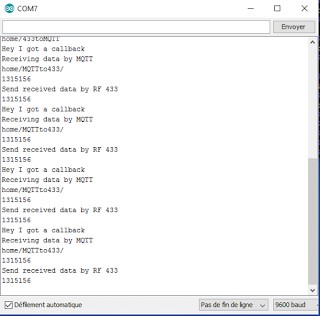
In this example, the Arduino receives the value 1315156 on the MQTT topic MQTTto433 and transmits the data via RF.
Similarly, when receiving data via 433MHz, the Arduino IDE serial monitor will show the received data:
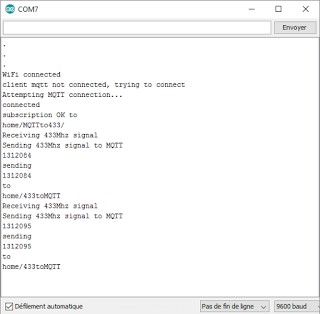
# Send data by MQTT with advanced RF parameters
RF sending supports three advanced parameters: bits length, RF protocol, and RF pulse length.
- To use a different bits number, include
"length":24in your payload. - To use a different RCSwitch protocol, include
"protocol":2in your payload. - To use a different pulse length, include
"delay":315in your payload.
Example:
mosquitto_pub -t "home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTto433" -m '{"value":1315156,"protocol":2,"length":24,"delay":315}'
This command will make RCSwitch use protocol 2 with a pulse length of 315ms and a bits number of 24.
# Repeat the RF signal several time
You can add a "repeat" key/value to the MQTTto433 JSON message to override the default number of repeats. Ensure that repeatRFwMQTT is enabled at compile time.
Example:
mosquitto_pub -t "home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTto433" -m '{"value":1315156,"protocol":1,"length":24,"delay":317,"repeat":10}'
# Set Transmit and Receive Frequency and Transmit Power of CC1101 Transceiver
The default transmit frequency of the CC1101 module is 433.92 MHz. This can be changed by including the desired frequency in the transmit message. The parameter is frequency, and valid values are 300-348 MHz, 387-464 MHz, and 779-928 MHz. Actual frequency support will depend on your CC1101 board.
Example:
mosquitto_pub -t "home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTto433" -m '{"value":1150,"protocol":6,"length":12,"delay":450,"repeat":8,"frequency":303.732}'
The default receive frequency of the CC1101 module is also 433.92 MHz. This can be changed by sending a message with the desired frequency. The parameter is frequency, and valid values are 300-348 MHz, 387-464 MHz, and 779-928 MHz. Actual frequency support will depend on your CC1101 board.
Example:
mosquitto_pub -t "home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoRF/config" -m '{"frequency":433.92}'
Messages received will include the frequency, and when transmitting on a different frequency, the module will return to the receive frequency afterward. For example, transmit messages on 303.732 MHz and then receive messages on 433.92 MHz.
Example received message:
{"value":4534142,"protocol":6,"length":26,"delay":356,"frequency":315.026}
You can also adjust the transmit power (tx-power) in decibels (dB) for a transmission. The parameter is cc1101_pa, and valid values in decibels are -30, -20, -15, -10, -6, 0, 5, 7, 10, 11, and 12. The default is the maximum value. Adjusting the transmit power can help reduce range and minimize disturbances with other nearby devices.
Example:
mosquitto_pub -t "home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTto433" -m '{"value":1315156,"protocol":2,"length":24,"delay":315,"cc1101_pa":5}'
# Pilight gateway
# Receiving data from RF signal
Subscribe to all the messages with mosquitto or open your MQTT client software:
sudo mosquitto_sub -t +/# -v
Generate your RF signals by pressing a remote button or other and you will see :
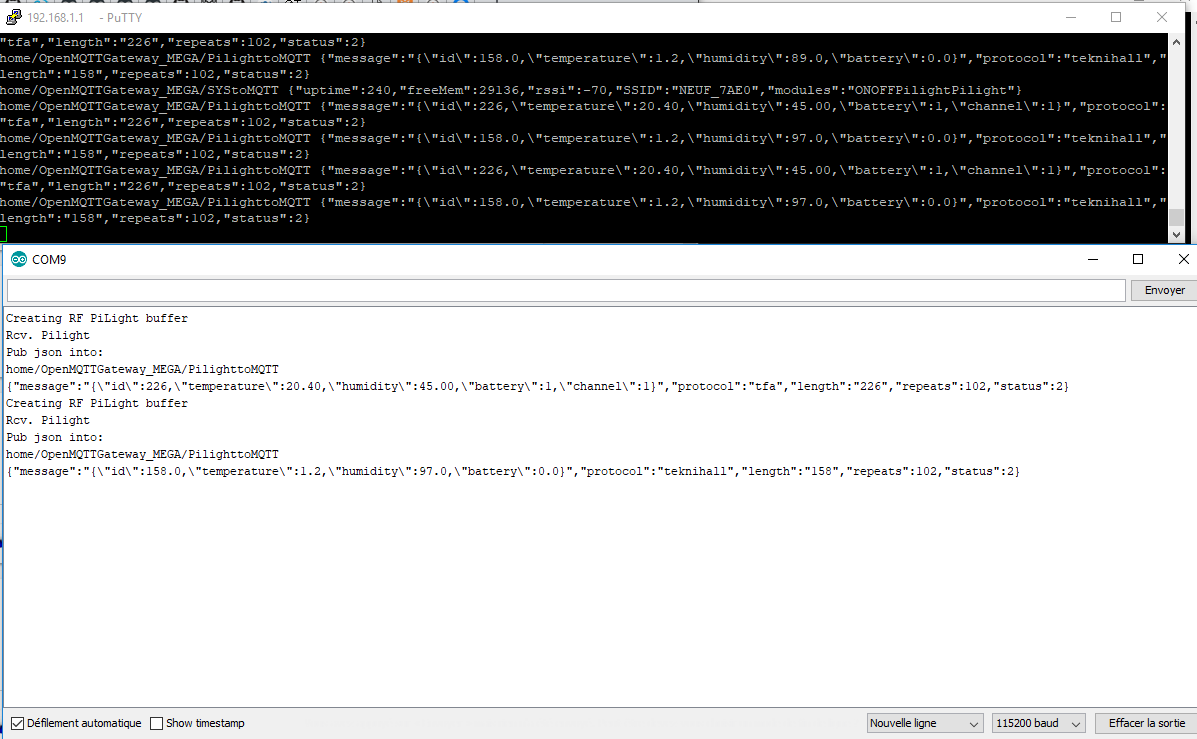
# Enabling RAW packet return support
First, you need to compile a binary with Pilight_rawEnabled true uncommented in config_RF.h.
Once the device is online and the active receiver is Pilght, you can toggle raw packet return. If current active receiver is not Pilight the toggle command will be ignored and harmless error message will be published.
You can turn on the RAW packet return support with the following MQTT command:
mosquitto_pub -t "home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoPilight/protocols" -m '{"rawEnabled":true}'
The returned JSON looks like this:
Client (null) received PUBLISH (d0, q0, r0, m0, 'home/OpenMQTTGateway/PilighttoMQTT', ... (176 bytes)) {"format":"RAW","rawlen":106,"pulsesString":"c:0102010102020202020101010101010102020201020102020202020201010101010101010101010102010102010201020201010203;p:521,944,1924,3845@"}
The pulseString format is Pilight's native. For those who are not familiar with it: c:* are the indexes for the p:* array, which are the different pulse length. (e.g. pulse[0] = 521ms, pulse[1]=944ms..., so c[0], which is a '0' = 521ms pulse, c[1], which is a '1' =944ms pulse etc)
After gathering all the packets you need, simply turn off the RAW packet support via MQTT:
mosquitto_pub -t "home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoPilight/protocols" -m '{"rawEnabled":false}'
# Limit Protocols
It is possible to limit the protocols that Pilight will respond to, this can help reduce noise from unwanted devices and in some cases disable conflicting protocols.
# Available protocols
To list the available protocols on the Serial -
mosquitto_pub -t "home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoPilight/protocols" -m '{"available":true}'
# Limit protocols
To limit the protocols, send a JSON array of protocols as below -
mosquitto_pub -t "home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoPilight/protocols -m '{"limit": ["array", "of", "protocols"]}'
eg: mosquitto_pub -t "home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoPilight/protocols" -m '{"limit":["tfa", "ev1527"}'
# Reset protocols
To reset and listen to all protocols -
mosquitto_pub -t "home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoPilight/protocols -m '{"reset": true}'
# Enabled protocols
To list the enabled protocols on the Serial -
mosquitto_pub -t "home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoPilight/protocols" -m '{"enabled":true}'
# Send data by MQTT to transmit a RF signal
# Using a known protocol
ON mosquitto_pub -t "home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoPilight" -m '{"message":"{\"systemcode\":12,\"unitcode\":22,\"on\":1}","protocol":"elro_400_switch"}'
OFF mosquitto_pub -t "home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoPilight" -m '{"message":"{\"systemcode\":12,\"unitcode\":22,\"off\":1}","protocol":"elro_400_switch"}'
These commands will transmit by RF the signals to actuate an elro_400 switch.
With a different frequency (CC1101 only):
mosquitto_pub -t "home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoPilight" -m '{"message":"{\"systemcode\":12,\"unitcode\":22,\"off\":1}","protocol":"elro_400_switch","frequency":315.026}'
# Using a raw signal
You can transmit raw signal data by using the "raw" protocol. This uses the Pilight pulse train string format. One such example string, representing a transmission for Nexus protocol weather stations, looks like this: c:03020202010102020102010101010101010202020201020102020202020101010201010202;p:500,1000,2000,4000;r:12@. This string represents pulses and gaps directly.
Each number in the list after p: that ends with ; stands for pulse and gap lengths in microseconds (µs). In this example, we have a list containing lengths of 500µs, 1000µs, 2000µs, and 4000µs.
Each number after c: and ended by ; represents a code that references the p: list by index. In this example, the first 4 numbers after c: are 0, 3, 0, and 2, which reference p:[0] = 500, p:[3] = 4000, p:[0] = 500, and p:[2] = 2000, respectively. In the language of digital radio transceiving, the most basic unit is usually a pulse and gap pair; in other words, 0s and 1s are represented by a pulse followed by a gap (lack of pulse) and the time lengths of these pulses and gaps. Different protocols have different pulse lengths and gap lengths representing 0, and a different one representing 1. Because of this pulse-gap nature, the codes in c: must be taken as pairs; the first number in a pair represents the length of the pulse, and the second number the subsequent gap. In this example, the first pair, 03, represents a pulse of 500µs followed by a gap of 4000µs. The next pair, 02, represents a pulse of 500µs followed by a gap of 2000µs.
The number after r: represents how many times the message in the string is to be repeated. The r: block is optional. The default number of repeats if r: is not specified is 10. Greater than about 100 repeats will cause a crash due to memory usage. If this example were written without specifying repeats, it would look like this: {"raw":"c:03020202010102020102010101010101010202020201020102020202020101010201010202;p:500,1000,2000,4000@"}
The entire string must end in a @. Each block must end in a ;, but if it is the last block in the string, the @ replaces the ;. Since the r: block is optional, this last block could be either p: or r:.
The JSON for the MQTT message to home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoPilight should specify the pulse train string as the value for the "raw" key: {"raw":"c:03020202010102020102010101010101010202020201020102020202020101010201010202;p:500,1000,2000,4000;r:12@"}.
e.g. mosquitto_pub -t "home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoPilight" -m '{"raw":"c:03020202010102020102010101010101010202020201020102020202020101010201010202;p:500,1000,2000,4000;r:12@"}'
# RF with SONOFF RF BRIDGE
# Receiving data from RF signal
Subscribe to all the messages with mosquitto or open your MQTT client software:
sudo mosquitto_sub -t +/# -v
Generate your RF signals by pressing a remote button or other and you will see:
home/OpenMQTTGateway/SRFBtoMQTT {"raw":"2B660186042E00E7E5","value":"59365","delay":"1111","val_Thigh":"390","val_Tlow":"1070"}
The first parameter is the raw value extracted from the RF module of the Sonoff bridge. The data are in hexadecimal and correspond to the details below: https://www.itead.cc/wiki/images/5/5e/RF_Universal_Transeceive_Module_Serial_Protocol_v1.0.pdf OpenMQTTGateway process the raw value to extract the other decimal values that can be reused to reproduce a signal (raw value can also be reused).
NOTE: currently the device doesn't receive correct values from Switches remote control
# Send data by MQTT to convert it on RF signal
mosquitto_pub -t "home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoSRFB" -m '{"value":1315156}'
This command will send by RF the code 1315156 and use the default parameters: Repeat = 1 Low time= 320 High time= 900 SYNC = 9500
# Send data by MQTT with advanced RF parameters
RF bridge sending support four advanced parameters; Repeat, Low time, High time & Sync if you want to repeat your signal sending put into your json payload "repeat":2, 2 means 2 repetitions of signal
if you want to use a low time of 315 put inside your json payload "Tlow":315
if you want to use a high time of 845 put inside your json payload "Thigh":845
if you want to use a sync time of 9123 put inside your json payload "Tsyn":9123
Example:
mosquitto_pub -t home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoSRFB/Tlow_315/Thigh_845/Tsyn_9123 -m '{"value":"33151562","delay":"9123","val_Thigh":"845","val_Tlow":"315"}'
will make RF Bridge send a signal with the use of listed parameters 315, 845, 9123...
mosquitto_pub -t home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoSRFB/Raw -m '{"raw":"267A013603B6140551"}'
will make RF Bridge send a signal with the use of advanced parameters defined in the raw string
# RF2 gateway KAKU
RF2 gateway enables to send command to RF devices with the KAKU protocol. DIO chacon devices are an example. It uses the same pinout as the RF gateway and both gateways can be used on the same setup.
Receiving RF codes with the KAKU protocol is not compatible with ZgatewayRF , so as to get the code of your remotes you should comment ZgatewayRF in User_config.h. Transmitting can be done with both ZgatewayRF and ZgatewayRF2
# Receiving data from KAKU signal
Subscribe to all the messages with mosquitto or open your MQTT client software:
sudo mosquitto_sub -t +/# -v
Generate your RF signals by pressing a remote button or other and you will see :
home/OpenMQTTGateway/RF2toMQTT {"unit":0,"groupBit":0,"period":273,"address":8233228,"switchType":0}
# Send data by MQTT to convert it on KAKU signal
Once you get the infos publish the parameters with MQTT like that for off:
mosquitto_pub -t home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoRF2 -m "{"unit":0,"groupBit":0,"period":273,"address":8233228,"switchType":0}"
for on:
mosquitto_pub -t home/OpenMQTTGateway/commands/MQTTtoRF2 -m "{"unit":0,"groupBit":0,"period":273,"address":8233228,"switchType":1}"